Nasdaq
Would you like to invest your money? Get in touch with an expert:
What is Nasdaq?
Nasdaq is an
American stock exchange that allows investors to buy and sell securities
electronically. Trading is entirely electronic, allowing investors to participate without the need for physical presence. To trade on the Nasdaq, an investor simply needs an account with a trading platform such as TD Ameritrade or E-Trade. The
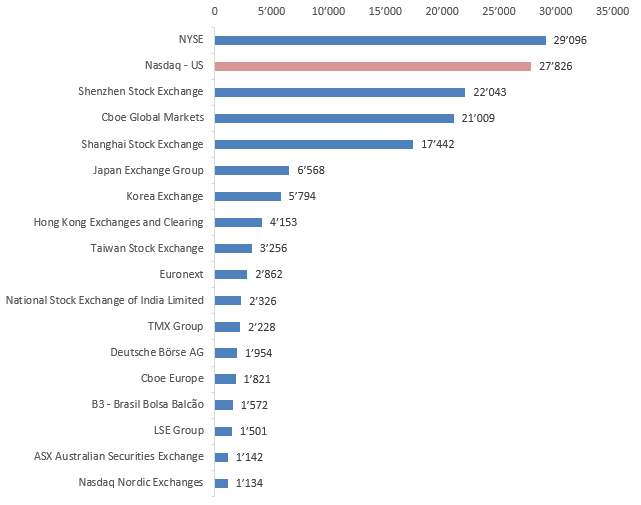
Nasdaq exchange ranks as the second-largest stock exchange in the world, based on market capitalization and trading volume in stocks for the year 2021. Trading takes place Monday through Friday between 9:30 am and 4:00 pm Eastern Time, with exceptions for major holidays. Since 2016, Adena Friedman has held the position of CEO of Nasdaq, making her the first woman to lead a major US stock exchange.
The world's largest stock exchanges by trading volume with stocks in 2021 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Source: www.statistia.com
The History of Nasdaq
Nasdaq was founded in 1971, marking an important milestone in the world of finance. At the same time, the Nasdaq Composite Index was introduced, making its debut on 5 February 1971. The name "Nasdaq" is an acronym for "National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations", reflecting its role in automating the trading of securities. Nasdaq originally operated as a subsidiary of the National Association of Securities Dealers (NASD), which is now recognized as the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA).
The founding of Nasdaq was driven by the Securities and Exchange Commission's (SEC) call for the automation of financial markets. The exchange's historical journey includes notable milestones:
- 1975: Nasdaq revolutionized the concept of Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) by listing companies funded by venture capital, enabling underwriting syndicates to serve as Market Makers.
- 1985: The Nasdaq introduced the Nasdaq-100 Index.
- 1996: Nasdaq took a digital leap by launching its first website, www.nasdaq.com.
- 1998: Nasdaq merged with the American Stock Exchange, forming the NASDAQ-AMEX Market Group. The American Stock Exchange was later acquired by NYSE Euronext in 2008, with its data integrated into the NYSE.
- 2000: Nasdaq's members voted to restructure, transforming the exchange into a publicly traded, profit-driven entity with shareholders, known as NASDAQ Stock Market Inc.
- 2007: Nasdaq made an international move by acquiring OMX, a Swedish-Finnish financial firm, and rebranded itself as NASDAQ OMX Group. NASDAQ OMX also acquired the Boston Stock Exchange.
- 2008: NASDAQ OMX extended its reach by acquiring the Philadelphia Stock Exchange, the oldest stock exchange in the United States.
- 2009: NASDAQ OMX has launched a mobile version of nasdaq.com, setting a new standard for the industry.
- 2016: Nasdaq expanded its portfolio by acquiring the International Securities Exchange (ISE), an equity options exchange.
Nasdaq, as a fully electronic exchange, does not rely on a physical trading floor. Instead, it established Nasdaq MarketSite in Times Square, Manhattan, as its center for digital financial activities.

Source: uxdesign.cc
Nasdaq Indices
Just like any other stock exchange, Nasdaq employs indices as essential tools. These indices are a compilation of various stocks and provide a snapshot of the current market performance. Nasdaq's primary indices are the Nasdaq Composite Index and the Nasdaq 100 Index. It's worth noting that both the NASDAQ Composite and the NASDAQ 100 include companies from the United States and abroad.
Nasdaq Composite Index
The Nasdaq Composite Index covers a wide range of over 3,000 stocks listed on the Nasdaq exchange. Its weighting is determined by market capitalization, providing a comprehensive view of the market. In particular, the index is heavily weighted towards the technology sector. Today, the Nasdaq Composite Index occupies a prominent place in financial market reporting. The chart illustrates the composition of the Nasdaq Composite Index at the end of April 2022. This index includes the well-known FAANG stocks: Meta Platforms, Amazon, Apple, Netflix and Alphabet. The ten most heavily weighted stocks in the Nasdaq Composite Index are Apple Inc., Microsoft Corp, Amazon.com Inc., Tesla Inc., Alphabet Class C, Alphabet Class A, Nvidia Corp, Meta Platforms, Broadcom Inc., and Costco Wholesale.
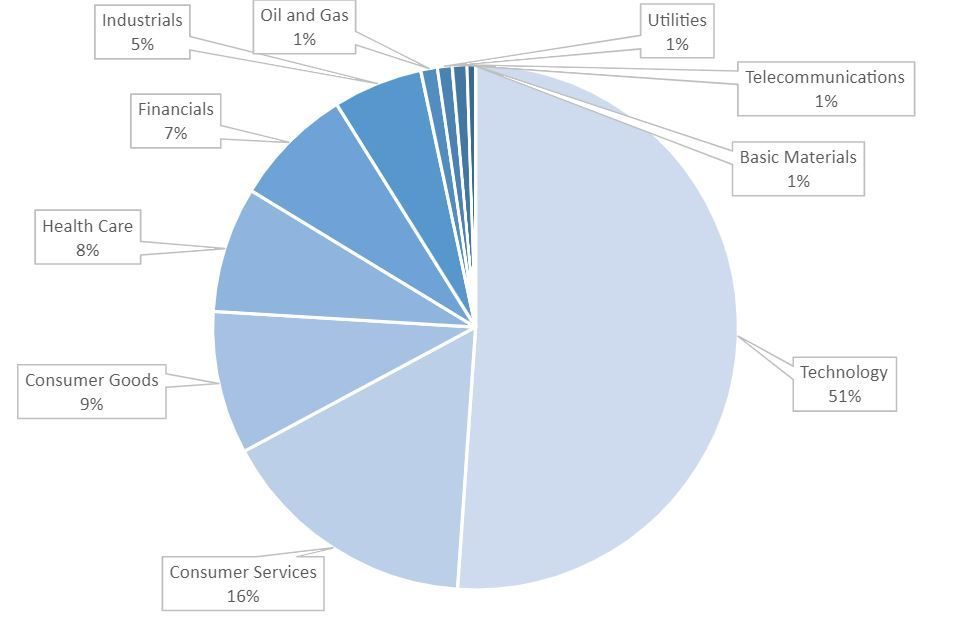
Source:
www.nasdaq.com
Nasdaq 100 Index
The Nasdaq 100 is an index that uses market capitalization as a weighting factor. In this approach, a company's weight in the index is determined by its market value. Consequently, the Nasdaq 100 consists of the 100 largest companies traded on the Nasdaq, ranked by their market capitalization. The leading companies in this index have a strong focus on the technology sector. Presently, the top 10 companies featured in the index include Apple Inc., Alphabet Class C, Alphabet Class A, Amazon.com Inc., Costco Wholesale, Broadcom Inc., Comcast Corp., Adobe Inc., Cisco Systems Inc., and Intel Corp. Annually, companies can be added to or removed from the Nasdaq 100 based on changes in their market value.
Would you like to invest your money?
Speak to an expert.
Your first appointment is free of charge.