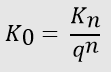Discounting
Would you like to invest your money? Get in touch with an expert:
What is Discounting?
The term discounting is used in financial mathematics. Discounting is the process of estimating the present value of an upcoming payment or cash flow. To put it another way, discounting is a method of calculating the present value of a future payment. Taking into account the time value of money, a franc has greater value today than tomorrow, since it can be invested in a variety of ways (time value of money). From a business perspective, an asset has value only if it is capable of producing future payments. Future payments are valued in today's terms by applying a discount factor. There is generally greater risk associated with an investment and its future payments when the discount factor is higher.
Example 1: Present Value of a One-Time Payment
Consider the case of an investor who invests CHF 100,000 in a property. There is a guarantee that the investor will be able to sell the property after three years for CHF 120,000. The interest rate used in the calculation is 5%. In order to determine whether this investment is worthwhile, the investor should calculate the present value of the future payment (CHF 120,000).
The calculation of the discount factor:
Discount factor: 1 / (1 + 0.05)³= 0.863837599
The discount factor is multiplied by the payment in 3 years:
CHF 120,000 * 0.863837599 = CHF 103,661
This investment is worthwhile since the present value of the future payment (CHF 103,661) is greater than the invested amount (CHF 100,000). Investing the money safely at 5% for three years would result in a value of CHF 115,763 (CHF 100,000 * (1+0.05)³). In comparison with the offered CHF 120,000, this amount is lower.
Example 2: Present Value of Multiple Payments
Consider the case of an investor who invests CHF 100,000 in a construction project on a one-time basis. The investor receives an annual payment surplus of CHF 40,000 for a period of three years. A five percent interest rate is used in the calculation.
The discount factor must be recalculated each year:
Discount factor year 1: 1 / (1 + 0.05) = 0.952380952
Discount factor year 2: 1 / (1 + 0.05)² = 0.907029478
Discount factor year 3: 1 / (1 + 0.05)³ = 0.863837599
Multiplying the discount factor by the payment per year yields the present value per year:
CHF 40,000 * 0.952380952 = CHF 38,095
CHF 40,000 * 0.907029478 = CHF 36,281
CHF 40,000 * 0.863837599 = CHF 34,554
The first payment is valued at CHF 38,095 today. The payment for the second year is worth CHF 36,281 today, while the payment for the third year is worth CHF 34,553. In total, CHF 108,930 will be generated. As this amount is greater than the original investment in this project (CHF 100,000), the investment is deemed to be worthwhile.
Would you like to invest your money?
Speak to an expert.
Your first appointment is free of charge.