Utility Sector
Would you like to invest your money? Get in touch with an expert:
What is the Utility Sector?
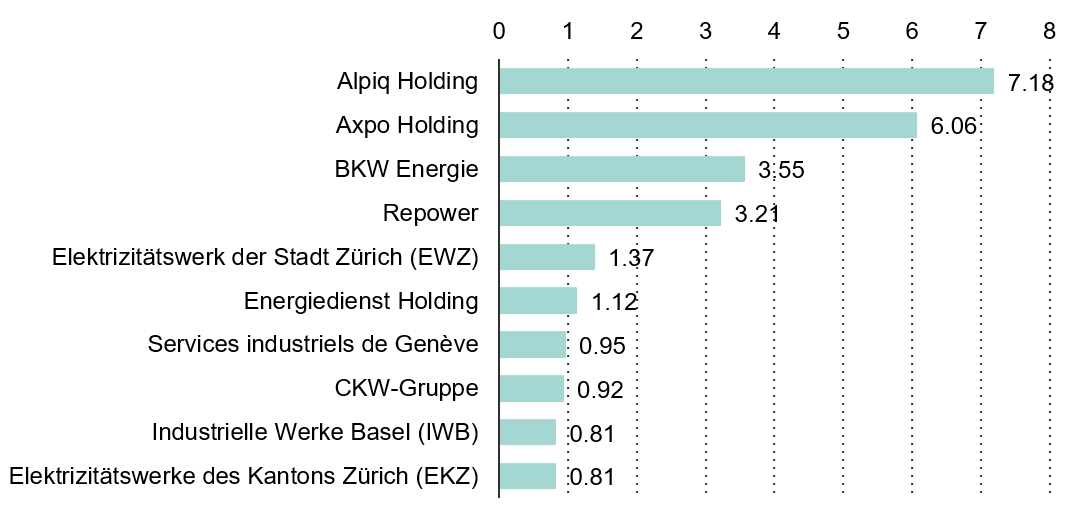
The utility sector includes companies providing essential services such as electricity, gas, and water. It includes companies responsible for both the generation and distribution of energy. Some utilities have adopted environmentally friendly practices, using sources such as wind turbines and solar panels to produce clean energy. The figure shows a collection of Switzerland's top energy providers and distributors, ranked by revenue for the year 2020/2021.
Selection of Leading Energy Providers/Distributors in Switzerland by Revenue (bn CHF) in 2020/2021
Source: www.statista.com
Investors who incorporate utility companies into their investment portfolios generally maintain long-term positions in these firms, frequently leveraging them for income generation via dividend payments. Utility companies typically exhibit diminished price volatility when compared to the broader stock markets. Price volatility, characterized by the standard deviation of price fluctuations, serves as a metric for gauging the extent of price fluctuations in a given stock. Diminished price volatility signifies that a stock's price is minimally impacted by market fluctuations. This is because the demand for utilities needs to be maintained in all economic conditions. Consequently, firms within the utility sector typically exhibit strong performance during economic downturns. However, they usually do not benefit from favorable economic conditions and may lag behind companies in other sectors during such periods. Thus, utility company stocks are well-suited for mitigating the risk within an investment portfolio. To this end, a proficient wealth manager can offer invaluable assistance in crafting an investment portfolio aligned with one's risk tolerance.
Companies in the utility sector require expensive infrastructure, leading to relatively high levels of debt. As a result, utility companies are highly sensitive to changes in market interest rates. Additionally, since July 2022, the rising inflation has had a negative impact on the utility sector.
Pros and Cons of the Utilities Sector
Investing in utilities offers distinct advantages, mainly due to their typically higher dividend payouts and resilience during economic downturns. As a result, utilities can be an effective diversifier for investment portfolios. However, utilities also have specific drawbacks, notably their high levels of debt, often necessitated by the costly infrastructure they operate. This debt burden exposes them to interest rate risk. To recap, here are the key points:
Advantages:
- Investment stability, even during economic downturns.
- Attractive, regularly paid dividends.
- A variety of investment options, including bonds, equities and ETFs.
Disadvantages:
- Strict regulatory oversight, which limits pricing flexibility.
- Significant capital requirements due to expensive infrastructure, resulting in high debt levels.
- Exposure to interest rate risk; rising interest rates may require higher yields to attract bond investors.
Would you like to invest your money?
Speak to an expert.
Your first appointment is free of charge.