What are dividends?
Dividends are a company’s way of distributingpart of its profits to its shareholders. In addition to companies, investment funds and ETFs also pay dividends. Payment is usually made in cash, but can also be made in the form of additionalshares.
Among other things, the dividend yield can also be used as a key figure to value a share, although one key figure alone is often not sufficient for a valuation and more comprehensive valuation models with several key figures should usually be used.
Which companies pay dividends?
A large, established company, where profits are more predictable, usually pays a high dividend.
Dividends are paid regularly in the following sectors in particular:
- Finance
- Oil, gas, energy
- Consumer goods
- Healthcare/pharmacy
In the case of start-ups or fast-growing companies (e.g. in the technology sector), it is less likely that a dividend will be paid. On the one hand, this is because research, development or expansions cause high costs and therefore no funds are available for dividend distributions. On the other hand, it makes little sense for growth companies with a high return on equity, for example, to reduce equity through dividend distributions, as this is likely to generate a higher return if it is used for further growth in the company instead of being distributed.
Reasons for dividend payments
Companies pay dividends for various reasons, e.g:
- For the purpose of shareholder retention, to encourage them to hold the shares for the long term.
- Dividends have a positive impact on the company – investor confidence is maintained and loyalty is increased. And: the dividend payment can attract new shareholders.
- With a high dividend payment, the company can indicate that business is going well and correspondingly high profits have been achieved.
- However, a high dividend could also be an indication that the company is not currently investing in new projects that will deliver even higher returns in the future – instead, the payout is made to shareholders.
- If an established company that has always paid dividends suddenly pays less or stops paying dividends altogether, this can be a sign that the company is in trouble.
- However, the reduction or elimination of the dividend does not necessarily indicate problems; after all, the company may have decided to use the profits for a new project that will generate a higher return for investors in the long term.
How do dividends affect the share price?
The dividend payment can have an impact on the share price, but it is not possible to make reliable predictions or general statements. For example, it is often the case that investors acquire shares in the company shortly before the Annual General Meeting in order to benefit from the dividend payment. This in turn can result in a sharp rise in the share price. It is also possible for companies to pay out dividends when their share price has fallen.
On the day after the Annual General Meeting, the company valueis reduced by the amount distributed. However, this does not affect the share price to the same extent, assupply anddemand and tax effects must also be taken into account.
Who determines how high the dividend is?
The profit generated by apublic limited company can be used for various purposes, e.g. to build up reserves or make investments. In addition, a portion can be distributed to the shareholders. The amount of this dividend is decided at the general meeting of the public limited company.
If the Annual General Meeting has approved the dividend, the dividend is paid out automatically three business days after the Annual General Meeting. However, in order to receive the dividend, shareholders must hold the shares in their securities account on the day of the Annual General Meeting.
What is the dividend yield?
The dividend yield is the ratio of the dividend per share to the current share price and can be calculated using the following formula:
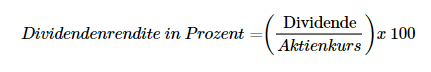
It shows the shareholder what profit the investment brings in terms of dividends.
The dividend yield can also help with the selection of shares: The dividend amount is of course not decided arbitrarily by the Annual General Meeting, but is based on the profitability of the company and its capital. A high dividend yield can therefore be an indication of a solid company with a good business performance (compared to companies in the same sector), which in turn makes it an attractive investment.
However, the dividend yield alone is not sufficient to evaluate a company. Other key figures should be used for this, such as
- Sales development
- Equity ratio
- Cuprofitratio
- Return on equity
- Free cash flow
- and much more.
When and how often are dividends paid?
Dividends are generally paid out annually by Swiss and German companies, while quarterly payments are common in the USA. When the dividend is paid is determined by the Annual General Meeting.
In addition to regular dividends, there may be one-off special dividends.
Dividend dates
The following dates are important for the payment of dividends:
Announcement date
On this day, the Executive Board decides on the distribution of a dividend and sets the payment date + record date.
Record date
This day determines which shareholders are entitled to receive the dividend. On the record date, the shareholders must be holders of the shares at the close of trading.
Ex-dividend date
Anyone who buys shares in the company on or after this date is no longer entitled to payment of the dividend.
Payment date
On this day, the announced dividend is paid out to the shareholders.

